Introduction to Septic Tanks
Septic tanks are a fundamental component of wastewater management systems, particularly in areas where centralized sewer systems are not available. These underground structures play a crucial role in treating and disposing of household wastewater. By separating solids from liquids, septic tanks facilitate the natural decomposition of waste, making them an eco-friendly option for rural and off-grid living. Understanding their function and maintenance requirements is essential for homeowners considering this sustainable solution.
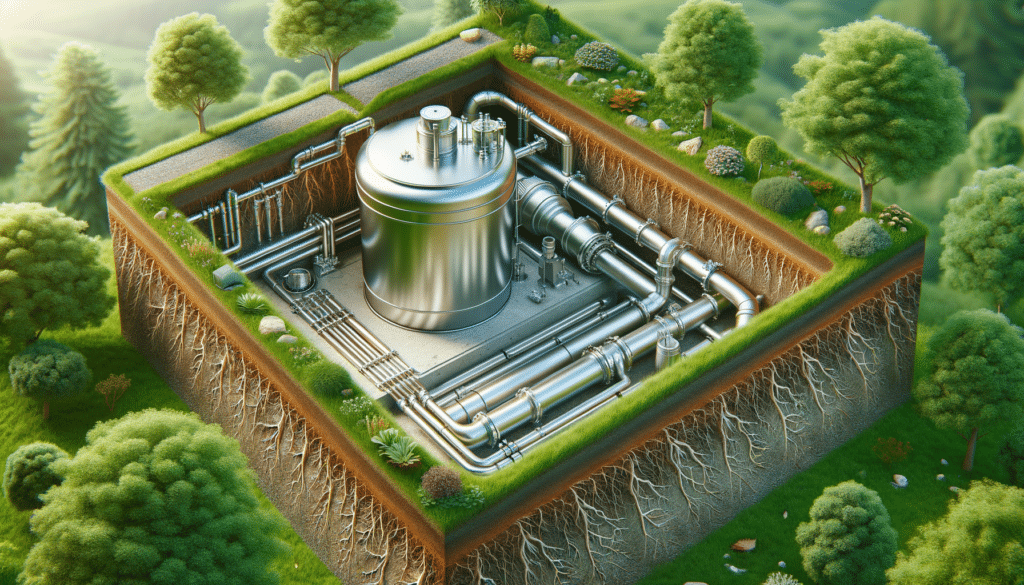
How Septic Tanks Work
At the heart of a septic system is the septic tank itself, a watertight container typically made of concrete, fiberglass, or polyethylene. Wastewater from a household flows into the tank, where solids settle at the bottom, forming sludge. Lighter materials, such as oils and grease, float to the top, creating a scum layer. The remaining liquid, or effluent, flows out into a drain field for further treatment.
The natural bacteria within the tank break down the solid waste, reducing its volume and preventing blockages. This process is crucial for maintaining the system’s efficiency and longevity. Regular inspection and pumping of the tank are necessary to ensure it functions correctly, preventing costly repairs or environmental hazards.
Septic Tank Waste Disposal
Proper disposal of septic tank waste is vital for environmental protection and public health. Once the tank is pumped, the waste, known as septage, must be treated and disposed of at a licensed facility. This process involves several steps, including:
- Transporting the waste to a treatment plant
- Separating liquids from solids
- Treating the waste to remove harmful pathogens
- Safely disposing of or repurposing the treated material
Efficient septic tanks manage household waste quietly, offering low-maintenance, eco-friendly wastewater solutions. By adhering to local regulations and guidelines, homeowners can ensure their septic system operates effectively, minimizing environmental impact.
Benefits of Septic Tanks
Septic tanks offer numerous advantages for homeowners, particularly in rural or remote areas. Some of the key benefits include:
- Cost-effectiveness: Once installed, septic systems require minimal maintenance and have lower operational costs compared to centralized sewer systems.
- Environmental sustainability: By promoting natural waste decomposition, septic tanks reduce the reliance on chemical treatments and energy-intensive processes.
- Independence: Septic systems offer a self-contained solution for wastewater management, ideal for properties not connected to municipal services.
These benefits make septic tanks a reliable choice for those seeking a sustainable and efficient wastewater management solution.
Maintaining Your Septic System
Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the longevity and efficiency of a septic system. Homeowners should adhere to the following practices:
- Schedule routine inspections and pumping every three to five years, depending on usage and tank size.
- Avoid flushing non-biodegradable items or chemicals that could disrupt the natural bacterial balance.
- Conserve water to prevent overloading the system, which can lead to failures and costly repairs.
By following these guidelines, homeowners can maintain a healthy septic system, ensuring efficient waste management and protecting the environment.